DC53 steel is a new general purpose cold work die and mold steel whose strength and toughness approach those of high-speed steels.
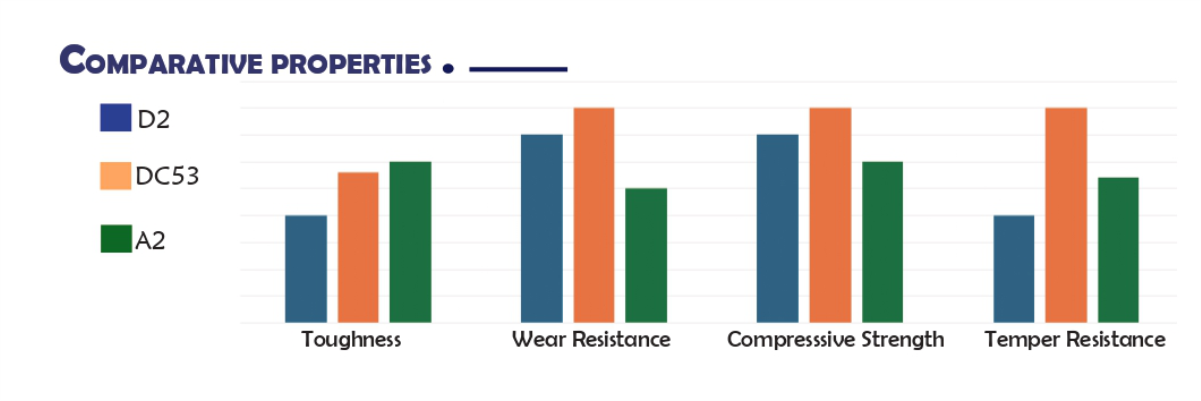
DC53 steel, is an improvement over alloy tool steel D2 specified in Standard (JIS) G4404. It eliminates the disadvantages of insufficient hardness and toughness, resulting from high-temperature tempering.D2 Supreme is a close equivalent to DC53 steel.
D2 Supreme is a cold work die and mold steel that has excellent machining characteristics, wear resistance, toughness, and compressive strength. It can produce a higher hardness than D2 after heat treatment and has greater wear resistance
| C | Cr | SI | Mn | Mo | V | P | S | |
| Min | 0.90 | 4.75 | 0.80 | 0.45 | 1.80 | 0.20 | -- | -- |
| Typical | 0.90 | 5.10 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 1.95 | 0.27 | ||
| Max | 1.05 | 5.50 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 2.10 | 0.35 | 0.025 | 0.025 |
APPLICATIONS
- » Gauges
- » Swagging Dies
- » Plastic Moulds
- » Rotor plates
- » Swagging Dies
- » Dies for cold forging
- » Piercing punch
- » Forming Dies
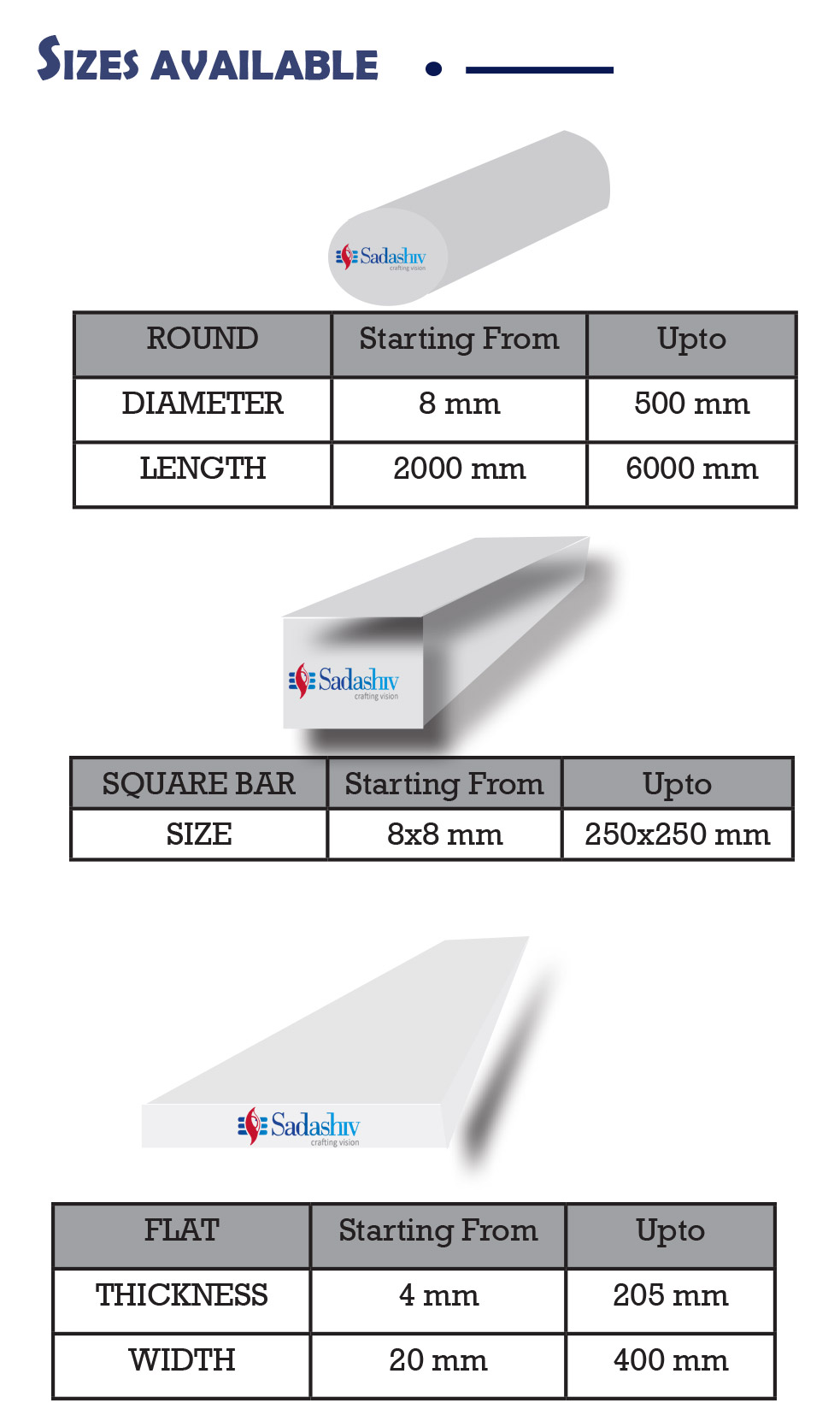
FORM SUPPLIED
- » Round bar
- » Sheets
- » Plates
- » Square Block
- » Flat bar
Available surface conditions : hot rolled, ground, peeled, turned, drawn, cold rolled
HEAT TREATMENT
- Welding : Lower minimum pre-and post – heating temperature than D2 reduces the incidence of weld. cracking and simplifies welding. Low hardness decline in heat affected zone minimises any deterioration in performance.
- Hardening Vacuum Furnace: Pre-heat to 300-400oC and then to 800-850oC allowing sufficient time to equalise. Raise to 1,020-1,040oC and allow soaking time.
- Quenching Vacuum Furnace: The high hardenability of this steel enables it to be satisfactorally quenched in a vacuum furnace.
- Tempering: As with D2, a third temper at400oC should be carried out to avoid any chance of any delayed grain growth and distortion. This is thepreferred
heat treatment for most applications as high hardness will be the primary consideration. Where maximum toughness is required, double temper between 200and 300oC (depending on application).
- Air Hardening – Air hardening DC53 is best accomplished under vacuum. First, preheat and hold at 800° C(1,475° F) to 850° C (1,560° F) until the part is uniformly heated and then increase the heat to 1,030° C (1,885°F) to Austenitize, otherwise known as soaking the tool.
- Salt Bath Hardening – Per-heat the part to 850° C (1,550° F) until uniformly heated. Austenitize in a molten salt bath at 1,030° C (1,885° F) for a minimum of 5 minutes. See chart below for details. Salt quench and then allowed to slowcool in still air to 45° C (120° F) to 65° C to (150° F) before tempering.
- Forging & Annealing – For special applications, DC53 can also be forged into many shapes. The temperature for forging is between 900° C (1,650° F) and 1,100° C (2,010° F). DC53 can be annealed by uniformly heating the part to 800° C (1,475° F) to 850° C (1,550° F), andholding for 2 hours followed by a slow cooling at no more than 27° C (50° F) degrees per hour to until the it has dropped below 500° C (930° F).
| Tool | Hardening | Tempering |
| single edge cutting tools | 1220 ºC | 550-570 ºC |
| multi edge cutting tools | 1180-1220 ºC | 550-570 ºC |
| cold work tools | 1050-1150 ºC | 550-570 ºC |
PROCESSING
DC53 can be worked as follows :
- Machining( grinding,turning,milling)
- Polishing
- Hot forming
- Electrical discharge machining
- Welding(special procedure incl. pre-heating & filler
materials of base material composition)
GRINDING
During Grinding, local heating of the surface, which can alter the temper, must be avoided. Grinding wheel manufacturers can provide advise on the choice of grinding wheels
SURFACE TREATMENT
Surface Treatments: such as CVD, PVD, TD and Nitriding require the use of relatively high processing temperatures. While this can be a problem with standard
D2, the higher through hardness of DC53
DELIVERY HARDNESS
- » Typical soft annealed hardness is 360-430 BHN
- » Cold drawn and cold rolled material is typically 10-40 HB harder